May 20, 2025
By: Brionna Benedetti, CPC, CRC
Download the full guide: Transplants and Amputations Coding Guide
High Blood Pressure vs. Hypertension
According to the American Heart Association, high blood pressure occurs when the force of the blood pumping through the heart is too high, causing that force to push against the walls of the blood vessels. A patient can have one reading of high blood pressure due to stress, anxiety, physical exertion, and many other factors, and not be diagnosed with hypertension. However, when this pressure is too high for a long period, it can damage the walls of the blood vessels and cause structural harm. A patient is diagnosed with hypertension when the readings are consistently high (chronic) and do not come down after rest.
Blood Pressure Levels
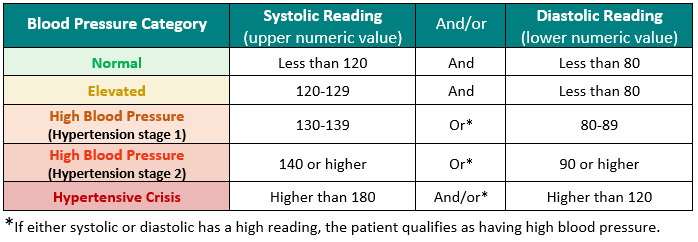
Documentation Requirements
To appropriately select a hypertension code, the following documentation requirements are needed:
- Type: There are many different types and causes of hypertension. For example, essential hypertension is entirely different from renovascular hypertension. Establishing the type is essential to code selection.
- Underlying causes: For secondary hypertension, it is also important to document the disease or condition that is causing the hypertension, as this affects code selection.
- Comorbidities: Hypertension can be complex and can come with comorbidities that make the treatment of the elevated blood pressure more difficult. For example, hypertension with heart disease is far more complicated than essential hypertension and is coded differently to account for the difference in severity. This is the same for hypertension with chronic kidney disease and hypertension with heart failure. To document comorbidities, associate using linking terms like “with”, “and”, “due to”, “associated with”, “complicated by”, etc.
Coding Guidelines
Hypertension requires a provider’s diagnosis to be billed on a claim. A coder cannot interpret a blood pressure reading and assume that the patient has hypertension without a formal diagnosis. If a patient has an elevated blood pressure reading without the formal hypertension diagnosis, code for the sign/symptom R03.0 Elevated blood-pressure reading, without diagnosis of hypertension.
When hypertension is documented, it is appropriate to code I10 essential hypertension, unless a comorbidity is present. Per chapter nine of the ICD-10-CM coding guidelines, there is an assumed causal correlation between hypertension and its comorbidities. Comorbidities that are linked to hypertension in the ICD-10-CM using the term “with”. Comorbidities found under the “with” below the code title should be interpreted to mean “associated with” or “due to.” This classification presumes a causal relationship between the two conditions even in the absence of provider documentation explicitly linking them. This means coders can code to higher specificity even when not directly correlated in providers’ documentation when a comorbidity is present. However, if the documentation clearly states that the two conditions are not related, then the combination code should not be selected.
Coding Guidelines

Hypertension requires a provider’s diagnosis to be billed on a claim. A coder cannot interpret a blood pressure reading and assume that the patient has hypertension without a formal diagnosis. If a patient has an elevated blood pressure reading without the formal hypertension diagnosis, code for the sign/symptom R03.0 Elevated blood-pressure reading, without diagnosis of hypertension.
When hypertension is documented, it is appropriate to code I10 essential hypertension, unless a comorbidity is present. Per chapter nine of the ICD-10-CM coding guidelines, there is an assumed causal correlation between hypertension and its comorbidities. Comorbidities that are linked to hypertension in the ICD-10-CM using the term “with”. Comorbidities found under the “with” below the code title should be interpreted to mean “associated with” or “due to.” This classification presumes a causal relationship between the two conditions even in the absence of provider documentation explicitly linking them. This means coders can code to higher specificity even when not directly correlated in providers’ documentation when a comorbidity is present. However, if the documentation clearly states that the two conditions are not related, then the combination code should not be selected.
| ICD 10 Code | Code Description | Code Also |
| I10 | Essential Hypertension | |
| Hypertension with Comorbidities | ||
| I11.0 | Hypertensive heart disease with heart failure | Use additional code to identify type of heart failure from code range I50.–. |
| I11.9 | Hypertensive heart disease without heart failure | any condition in I51.4-I51.7, I51.89, I51.9 due to hypertension |
| I12.0 | Hypertensive chronic kidney disease with stage 5 chronic kidney disease or end stage renal disease | Use additional code to identify the stage of chronic kidney disease (N18.5, N18.6). |
| I12.9 | Hypertensive chronic kidney disease with stage 1 through stage 4 chronic kidney disease, or unspecified chronic kidney disease | Use additional code to identify the stage of chronic kidney disease (N18.1-N18.4, N18.9). |
| I13.0 | Hypertensive heart and chronic kidney disease with heart failure and stage 1 through stage 4 chronic kidney disease, or unspecified chronic kidney disease | Use additional code to identify type of heart failure (I50.-) and stage of chronic kidney disease (N18.1-N18.4, N18.9). |
| I13.10 | Hypertensive heart and chronic kidney disease without heart failure, with stage 1 through stage 4 chronic kidney disease, or unspecified chronic kidney disease | Use additional code to identify the stage of chronic kidney disease (N18.5, N18.6). |
| I13.11 | Hypertensive heart and chronic kidney disease without heart failure, with stage 5 chronic kidney disease, or end stage renal disease | Use additional code to identify the stage of chronic kidney disease (N18.5, N18.6). |
| I13.2 | Hypertensive heart and chronic kidney disease with heart failure and with stage 5 chronic kidney disease, or end stage renal disease | Use additional code to identify type of heart failure (I50.-) and he stage of chronic kidney disease (N18.5, N18.6) |
| Secondary Hypertension | ||
| I15.0 | Renovascular hypertension | Code also underlying condition causing the hypertension. |
| I15.1 | Hypertension secondary to other renal disorders | Code also underlying condition causing the hypertension. |
| I15.2 | Hypertension secondary to endocrine disorders | Code also underlying condition causing the hypertension. |
| I15.8 | Other secondary hypertension | Code also underlying condition causing the hypertension. |
| I15.9 | Secondary hypertension, unspecified | Code also underlying condition causing the hypertension. |
Quality Performance and Exclusions
CPT II Coding for Quality
To be able to submit the CPT II codes of a patient’s blood pressure reading for HEDIS measures, the encounter must list the hypertension diagnosis, the date the vitals were taken, and the blood pressure results. Compliant readings can come from outpatient visits, virtual or telephonic visits, remote monitoring events, and other non-acute or inpatient visits. To report a patient’s blood pressure reading, you must code two separate CPT II codes- one for the systolic reading and one for the diastolic reading. If multiple readings are taken on the same day, report the lowest of both the systolic and diastolic readings taken:
| Systolic | Diastolic | ||
| 3074F | Systolic reading less than 130mm Hg | 3078F | Diastolic reading of less than 80 mm HG |
| 3075F | Systolic reading between 130-139 mm HG | 3079F | Diastolic reading between 80-89 mm HG |
| 3077F | Systolic reading greater than or equal to 140 mm Hg | 3080F | Diastolic reading greater than or equal to 90 mm Hg |
What are Exclusions?
Quality measures utilize exclusions when an advanced illness impacts the quality of life for a patient to the point where preventative screenings and disease-specific monitoring become less important to maintaining daily function and quality of life for a patient’s declining health status. These exclusions change the eligible population (denominator) for select measures.
How do Exclusions relate to Controlling Blood Pressure?
This measure can be positively affected, as coding to the highest level of specificity can directly aid your quality scores! By coding hypertension with complications, along with a frailty code (if applicable to the patient), you are effectively pulling the patient out of the measure and will not have your quality scores adversely impacted due to uncontrolled blood pressure results.
Below are examples of when a patient could be excluded from a measure:
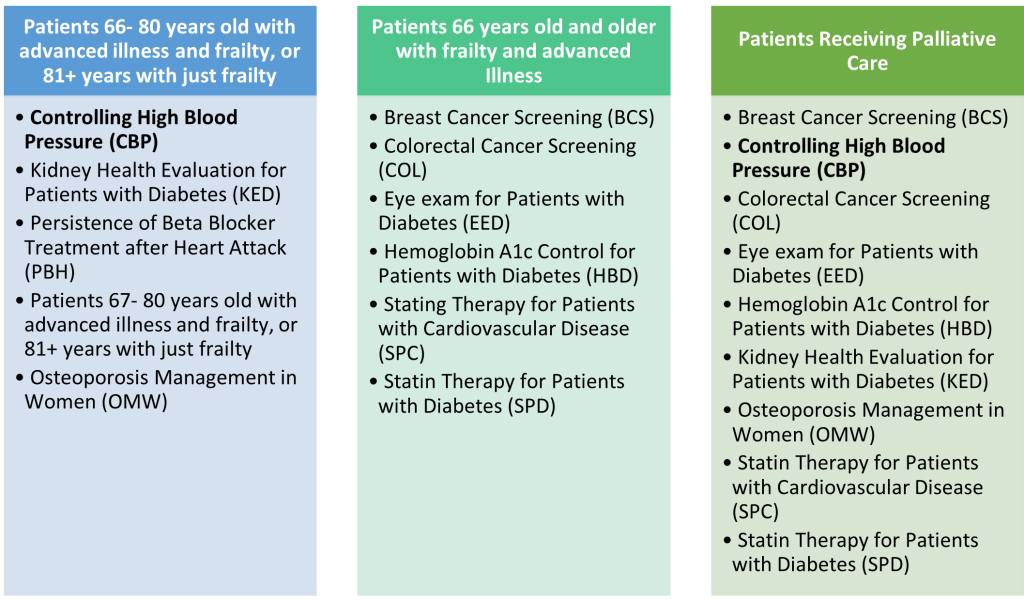
When excluding a patient from one HEDIS quality measure using advanced illness and frailty exclusions, a patient will be excluded from all applicable quality measures in which they are in the denominator. It is important to look at how excluding one patient could affect all the denominators of the quality gaps.
How are Exclusions Identified?
Exclusions can only be identified and removed by insurance payers through claim submissions. Codes from the National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA) Advanced Illness Value Set and/or Frailty Value Sets for devices, diagnoses, encounters, and symptoms are used to identify patients who will be removed from a measure denominator.
To exclude a patient from a measure, you must bill an advanced illness coded twice in the calendar year, with a frailty code also coded and billed twice in the calendar year. These two codes must be captured on a claim at two separate outpatient visits, two observation or non-acute inpatient visits, one acute inpatient visit, or be given one dispensed dementia medication to qualify. Palliative care exclusions are based on any single claim with a palliative care code submitted during the current measurement year.
| Advanced Illness Codes for Hypertension | ||
| I11.0 | ICD-10 | Hypertensive heart disease with heart failure |
| I12.0 | ICD-10 | Hypertensive chronic kidney disease with stage 5 chronic kidney disease or end-stage renal disease |
| I13.0 | ICD-10 | Hypertensive heart and chronic kidney disease with heart failure and stage 1 through stage 4 chronic kidney disease, or unspecified chronic kidney disease |
| I13.11 | ICD-10 | Hypertensive heart and chronic kidney disease without heart failure, with stage 5 chronic kidney disease, or end-stage renal disease |
| I13.2 | ICD-10 | Hypertensive heart and chronic kidney disease with heart failure and with stage 5 chronic kidney disease, or end-stage renal disease |
Frailty Code Set
| Code | Code Type | Code Description |
| L89.000 – L89.96 | ICD-10 | Pressure ulcers |
| M62.50 | ICD-10 | Muscle wasting and atrophy, not elsewhere classified, unspecified site |
| M62.81 | ICD-10 | Muscle weakness (generalized) |
| M62.84 | ICD-10 | Sarcopenia |
| R26.0 | ICD-10 | Ataxic Gate |
| R26.1 | ICD-10 | Paralytic Gait |
| R26.2 | ICD-10 | Difficulty in Walking, not elsewhere classified |
| R26.89 | ICD-10 | Other abnormalities of gait and mobility |
| R26.9 | ICD-10 | Unspecified abnormalities of gait and mobility |
| R41.81 | ICD-10 | Age-related Cognitive Decline |
| R53.1 | ICD-10 | Weakness |
| R53.81 | ICD-10 | Other malaise |
| R53.83 | ICD-10 | Other fatigue |
| R54 | ICD-10 | Age-related physical debility |
| R62.7 | ICD-10 | Adult failure to thrive |
| R63.4 | ICD-10 | Abnormal weight loss |
| R63.6 | ICD-10 | Underweight |
| R64 | ICD-10 | Cachexia |
| Falls | ||
| W01.0 | ICD-10 | Fall on same level from slipping, tripping and stumbling without subsequent striking against object |
| W01.10 | ICD-10 | Fall on same level from slipping, tripping and stumbling with subsequent striking against unspecified object |
| W01.110 | ICD-10 | Fall on same level from slipping, tripping and stumbling with subsequent striking against sharp glass |
| W01.111 | ICD-10 | Fall on same level from slipping, tripping and stumbling with subsequent striking against power tool or machine |
| W01.118 | ICD-10 | Fall on same level from slipping, tripping and stumbling with subsequent striking against other sharp object |
| W01.119 | ICD-10 | Fall on same level from slipping, tripping and stumbling with subsequent striking against unspecified sharp object |
| W01.190 | ICD-10 | Fall on same level from slipping, tripping and stumbling with subsequent striking against furniture |
| W01.198 | ICD-10 | Fall on same level from slipping, tripping and stumbling with subsequent striking against other object |
| W06. | ICD-10 | Fall from bed |
| W07. | ICD-10 | Fall from chair |
| W08. | ICD-10 | Fall from other furniture |
| W10.0 | ICD-10 | Fall (on)(from) escalator |
| W10.1 | ICD-10 | Fall (on)(from) sidewalk curb |
| W10.2 | ICD-10 | Fall (on)(from) incline |
| W10.8 | ICD-10 | Fall (on)(from) other stairs and steps |
| W10.9 | ICD-10 | Fall (on)(from) unspecified stairs and steps |
| W18.00 | ICD-10 | Striking against unspecified object with subsequent fall |
| W18.02 | ICD-10 | Striking against glass with subsequent fall |
| W18.09 | ICD-10 | Striking against other object with subsequent fall |
| W18.11 | ICD-10 | Fall from or off toilet without subsequent striking against object |
| W18.12 | ICD-10 | Fall from or off toilet with subsequent striking against object |
| W18.2 | ICD-10 | Fall in (into) shower or empty bathtub |
| W18.30 | ICD-10 | Fall on same level, unspecified |
| W18.31 | ICD-10 | Fall on same level due to stepping on an object |
| W18.39 | ICD-10 | Other fall on same level |
| W19. | ICD-10 | Unspecified fall |
| Y92.199 | ICD-10 | Unspecified place in other specified residential institution as the place of occurrence of the external cause |
| Z59.3 | ICD-10 | Problems related to living in residential institution |
| Z73.6 | ICD-10 | Limitation of activities due to disability |
| Z74.01 | ICD-10 | Bed confinement status |
| Z74.09 | ICD-10 | Other reduced mobility |
| Z74.1 | ICD-10 | Need for assistance with personal care |
| Z74.2 | ICD-10 | Need for assistance at home and no other household member able to render care |
| Z74.3 | ICD-10 | Need for continuous supervision |
| Z74.8 | ICD-10 | Other problems related to care provider dependency |
| Z74.9 | ICD-10 | Problem related to care provider dependency, unspecified |
| Z91.81 | ICD-10 | History of falling |
| Z99.11 | ICD-10 | Dependence on respirator [ventilator] status |
| Z99.3 | ICD-10 | Dependence on wheelchair |
| Z99.81 | ICD-10 | Dependence on supplemental oxygen |
| Z99.89 | ICD-10 | Dependence on other enabling machines and devices |
Sources
- What is High Blood Pressure? | American Heart Association
- High blood pressure vs hypertension: what’s the difference? | American Heart Association
- FY2022 April 1 update ICD-10-CM Guidelines
Find more coding guides at https://chpanetwork.com/guides-tools/.




